Категория: Новости.
by D. Pankin, M. Smirnov, A. Povolotckaia, A. Povolotskiy, E. Borisov, M. Moskovskiy, A. Gulyaev, S. Gerasimenko, A. Aksenov, M. Litvinov and A. Dorochov
Materials 2022, 15(2), 649;
https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15020649
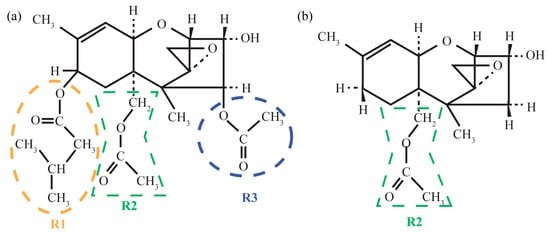
This paper discusses the applicability of optical and vibrational spectroscopies for the identification and characterization of the T-2 mycotoxin. Vibrational states and electronic structure of the T-2 toxin molecules are simulated using a density-functional quantum-mechanical approach. A numerical experiment aimed at comparing the predicted structural, vibrational and electronic properties of the T-2 toxin with analogous characteristics of the structurally similar 3-deacetylcalonectrin is performed, and the characteristic spectral features that can be used as fingerprints of the T-2 toxin are determined. It is shown that theoretical studies of the structure and spectroscopic features of trichothecene molecules facilitate the development of methods for the detection and characterization of the metabolites.
Категория: Новости.
by D. Pankin, M. Smirnov, A. Povolotckaia, A. Povolotskiy, E. Borisov, M. Moskovskiy, A. Gulyaev, A. Lavrov and A. Izmailov
Agronomy 2021, 11(12), 2402;
https://doi.org/10.3390/agronomy11122402
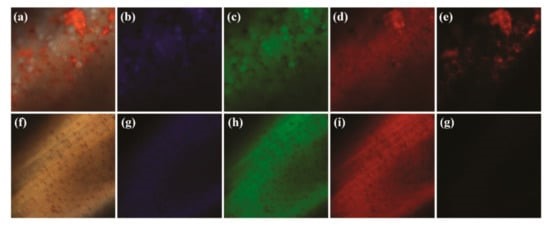
At present, one of the critical problems in agriculture is the identification of cereals, including oats, infected by Fusarium spp. genus fungi. Timely diagnostics can prevent the further disease spread and help to identify the already stored infected grains. In this regard, the aim of this work is to develop the spectroscopic approaches that determine the infected grains. As an object of the investigation the “Zalp” cultivar oat, both healthy and infected grains of the 2020 harvest were chosen. The spectroscopic diagnostics included FTIR in the mid-IR region, Raman, and luminescence methods. Combination of chemometric tools with FTIR and Raman spectroscopy allowed obtaining approaches based on identified characteristic spectral features which may be used as infection markers. These approaches make it possible to detect the infection on the grain husk. The carotenoid type fungi pigment was identified within the resonance conditions of Raman scattering excitation. The luminescence study of infected oat husk revealed the presence of characteristic chlorophyll α peak which is absent in healthy grain husk.
Категория: Новости.
by M. Galimova, E. Zueva, A. Dobrynin, I. Kolesnikov, R. Musin, E. Musina A. Karasik
Dalton Trans., 2021,50, 13421-13429
doi: 10.1039/D1DT02344F
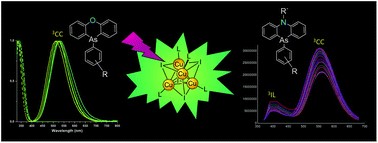
Two luminescent Cu4I4-cubane tetramers with N-methyl-10-(p-halogenophenyl)-5,10-dihydrophenarsazine ligands were synthesized and characterized by NMR spectroscopy, mass spectrometry, elemental analysis, and single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis. The UV–Vis absorption and emission properties were studied and rationalized by DFT and time-dependent DFT calculations. The luminescence behavior was found to be rather different from that of recently reported tetranuclear copper iodide cubane clusters based on As,O-analogues – 10-(aryl)phenoxarsines. The crystalline powders of both complexes exhibit the temperature-dependent dual-band emission: the low-energy emission originates from the cluster-centered (3CC) triplet state, whereas the high-energy emission was attributed to the intraligand (3IL) triplet state.
Категория: Новости.
by Pankin, D., Povolotckaia, А., Borisov, E., Rongonen, S., Mikhailova, А., Tkachenko, T., Doledova, N., Rylkova, L., Kurochkin, A.
Journal of Cultural Heritage, 51, 125-131
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.culher.2021.08.005
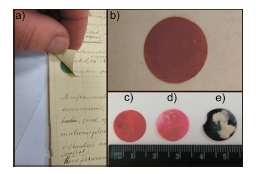
This work is devoted to the study of the composition of such a characteristic object for the 17–19 centuries as wafers, which were used to join sheets of paper in documents or to seal letters. Owing to the limited information in the literature and possible degradation processes that may occur with them in this paper, the modern optical techniques were applied to gain information about them. As the object of the investigation the wafers found in the hand-written documents of Academician Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve (Vasily Yakovlevich Struve 1793–1864) were chosen (Fund number 721, the RAS Archive, Saint-Petersburg branch, Struve V.). Besides the common way it was found that a large number of colored wafers were used to join several sheets in one composite elongated document and also to make correction on top of what was written. As the part of a major task aimed at maintaining the fund documents dated 19th century and the stability of the used joining wafers in particular the Raman and UV–Vis absorbance spectroscopies were applied in order to investigate wafers chemical composition. It was found the use of two different types of pigments for orange hues. One of them is cinnabar and another one is made up of red lead and massicot mixture. The Prussian blue was used for wafers with dark blue hue and as a mixture with massicot for green hue. According to UV–Vis absorbance spectroscopy it was found the use of anthraquinone type pigment for the red, rose and purple hues. The presence of the wafers with different base materials were determined by means of the Raman spectroscopy, namely of the vegetable (presumably starch) and protein (presumably gelatin) origin. The obtained results were compared with the data available in the previous researches, including the recipes given in the publications of the 19th century.
Категория: Новости.
Sensors and Actuators A: Physical Vol. 325, 112722
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sna.2021.112722
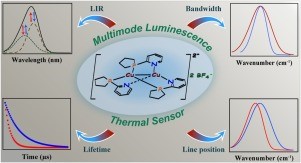
Luminescence thermometry became one of the most rapidly developing scientific areas in the last decade. A lot of scientific groups are working on the design of a highly sensitive and accurate thermometer based on monitoring the chosen luminescence parameter. However, it is still a challenge to create a multimode sensor utilizing several temperature-dependent parameters for thermometry, which could broaden the working range and improve thermometric characteristics. Here, we successfully demonstrate the binuclear helical charged complex [L3Cu2](BF4)2 (L = 1-pyridine-2-ylphospholane) in head-to-head configuration with solid-state single-band emission as a multimode optical thermometer. Thermal sensing was provided using luminescence intensity ratio, spectral line position, bandwidth, and lifetime. Ratiometric temperature determination was performed by the successful use of deconvolution analysis. The thermometric performance was studied in terms of relative thermal sensitivity, which was varied from 0.93 % K−1 for line position to 0.11 % K−1 for bandwidth at 298 K. The obtained results show Cu(I) complex as a cheap multimode luminescence thermal sensor in the 98–393 K range.


 Русский (РФ)
Русский (РФ)  English (UK)
English (UK) 


