Категория: Новости.
В РЦ ОЛМИВ Научного парка СПбГУ завершены работы по договору №33ЕП/2022 от 02.09.2022 на выполнение научно-исследовательских работ в рамках Соглашения Федерального государственного бюджетного научного учреждения «Федеральный научный агроинженерный центр ВИМ» и Минобрнауки России № 075-15-2020-774 от 07.10.2020 по теме «Разработка экологически безопасных и энергоэффективных спектральных и лазерных технологий для увеличения продуктивности сельскохозяйственных растений и животных». В данном проекте СПбГУ в соответствии с соглашением о Консорциуме является соисполнителем работ.
В 2022 году в рамках выполнения данных договорных работ опубликована статья коллективом соавторов из РЦ ОЛМИВ и ВИМ:
D. Pankin, M. Smirnov, A. Povolotckaia, Alexey P., E. Borisov, M. Moskovskiy, A. Gulyaev, S. Gerasimenko, A. Aksenov, M. Litvinov and A. Dorochov, «DFT modelling of molecular structure, vibrational and UV-Vis absorption spectra of T-2 toxin and 3-deacetylcalonectrin» // Materials. – 2022. – Т. 15. – №. 2. – С. 649. DOI: 10.3390/ma15020649 https://www.mdpi.com/1996-1944/15/2/649
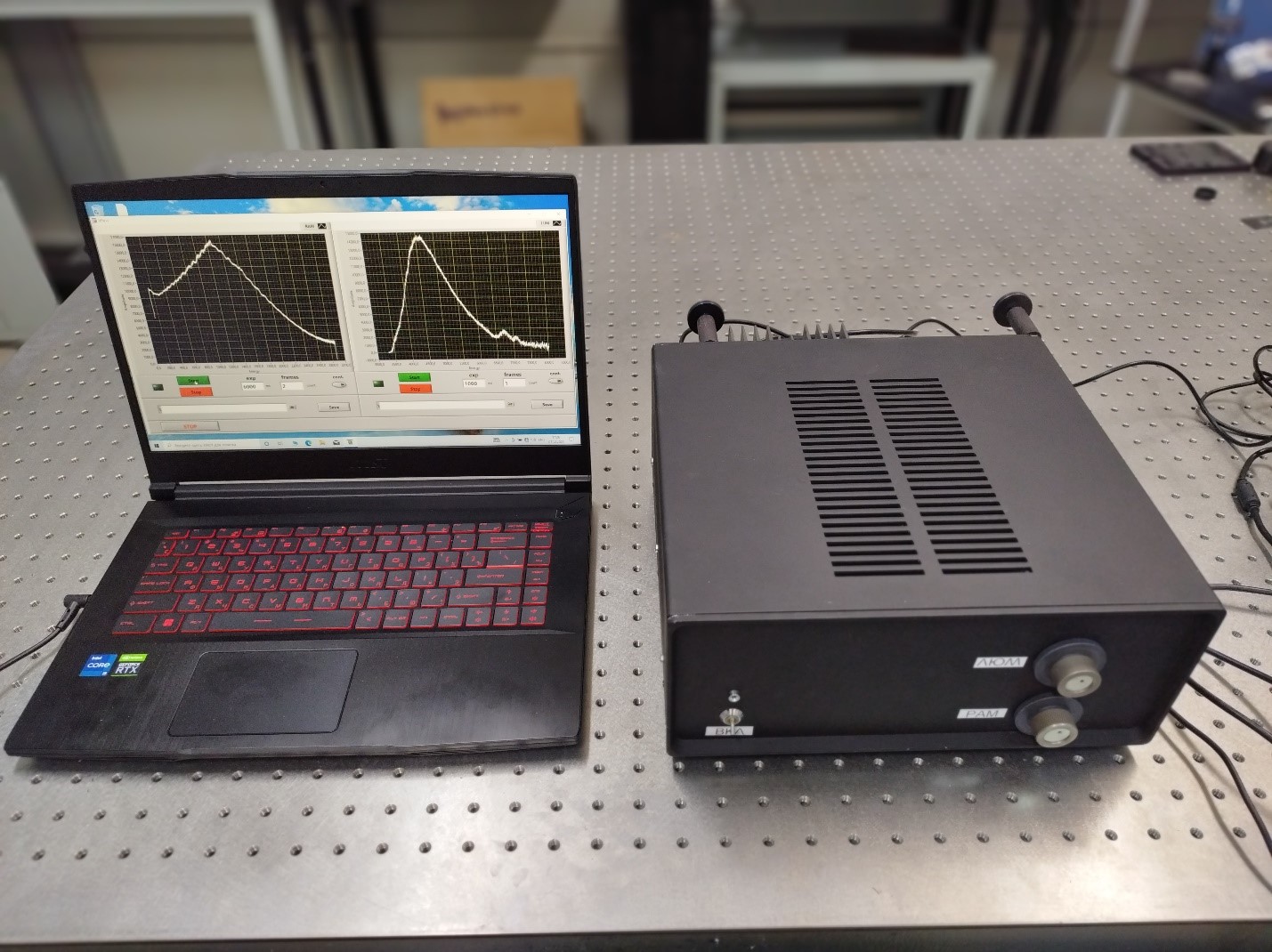
Кроме того, в РЦ ОЛМИВ разработан и изготовлен действующий макет портативного исполнительного устройства, способного различать кондиционные и зараженные семена методами Рамановской и люминесцентной спектроскопии.

Категория: Новости.
Поздравляем специалиста РЦ ОЛМИВ Бикбаеву Гулию Ильнуровну с успешной защитой магистерской диссертации по теме «Лазерный синтез периодических массивов плазмонных наноструктур для сенсорных приложений» на кафедре Лазерной Химии и Лазерного материаловедения Института Химии СПбГУ. Желаем дальнейших научных успехов и открытий! Желаем не останавливаться на достигнутом!

Категория: Новости.
by I. Shubina, I. Kolesnikov, P.Olshin, M. Likholetova, M. Mikhailov, A. Manshina, D. Mamonova
Ceramics International Vol. 48, Iss. 11, pp. 15832-15838
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2022.02.121
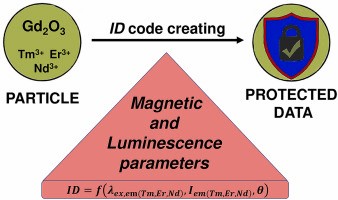
Development of novel materials with advanced properties is one of the main research directions of chemistry. New substances are not only crucial for many current technological applications but also should satisfy the needs of tomorrow. Industry often requires reliable, economically effective methods that can provide high quality reproducible results. Here we propose an inexpensive synthesis method that is suitable for synthesis of many types of particles. In this work we focused on Gd2O3:Tm3+, Er3+, Nd3+ particles with luminescence and magnetic properties. Based on the analysis of morphology, structural and optical properties of particles prepared by the standard Pechini methods and its variations, we found that the method with K2CO3 as additive yields particles with smaller sizes (down to tens of nm), higher crystallinity, and up to 1.7 times increased luminescence intensity. We also demonstrate that the unique combination of the particles’ characteristics, for example, the intensity ratio of the luminescent bands corresponding to different REI and the mass susceptibility, strongly depends on the composition, synthesis method, and structure. The variety of the combination of the properties makes these particles a promising candidate for safety markers applications.
Категория: Новости.
Сотрудники РЦ ОЛМИВ Поволоцкая А.В., Михайлова А.А и Капуткина С.Ю. прошли курсы повышения квалификации в рамках семинара «Новейшие разработки в области аналитического оборудования для исследования и контроля качества материалов». Организатор семинара компания ООО «Мелитек».
Категория: Новости.
by A. Miroshnichenko, K. Deriabin, A. Baranov, V. Neplokh, D. Mitin, I. Kolesnikov, M. Dobrynin, E. Parshina, I. Mukhin, R. Islamova
ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2022, 4, 4, 2683–2690
https://doi.org/10.1021/acsapm.2c00017

Light-excited flexible and self-healing luminescent polymers have attracted extensive attention for developing advanced color-emitting films. Luminophores on the base of lanthanide(III)-incorporating polysiloxanes exhibit a high photoresponse and can be applied for controlled color lighting in flexible device applications. We present red-, green-, and blue-emitting Eu3+, Tb3+, and Tm3+-bipyridinedicarboxamide-co-polydimethylsiloxanes (Ln-Bipy-PDMS) produced with a two-step procedure of polycondensation and complexation. Bipyridinic ligands provide formation of coordinatively saturated complexes of lanthanide ions and strong photoluminescence (PL) in the case of Eu3+ and Tb3+. The thin Ln-Bipy-PDMS films are studied as ultraviolet-light converters, which can be mechanically stacked one above another to achieve the desired color. We demonstrate that these stacks can have intense PL in the spectral range from green to yellow and red. Due to the structural features, Ln-Bipy-PDMS also demonstrate a relatively high tensile (approximately 1.5 MPa) and elongation at break (approximately 185%) and non-autonomous self-healing on heating. The self-healing properties of Ln-Bipy-PDMS enable the stacking of films into monoliths with the required color of PL. Such systems do not require any synthesis stages, and a one-healed monolith film possesses two luminescence colors.


 Русский (РФ)
Русский (РФ)  English (UK)
English (UK) 




